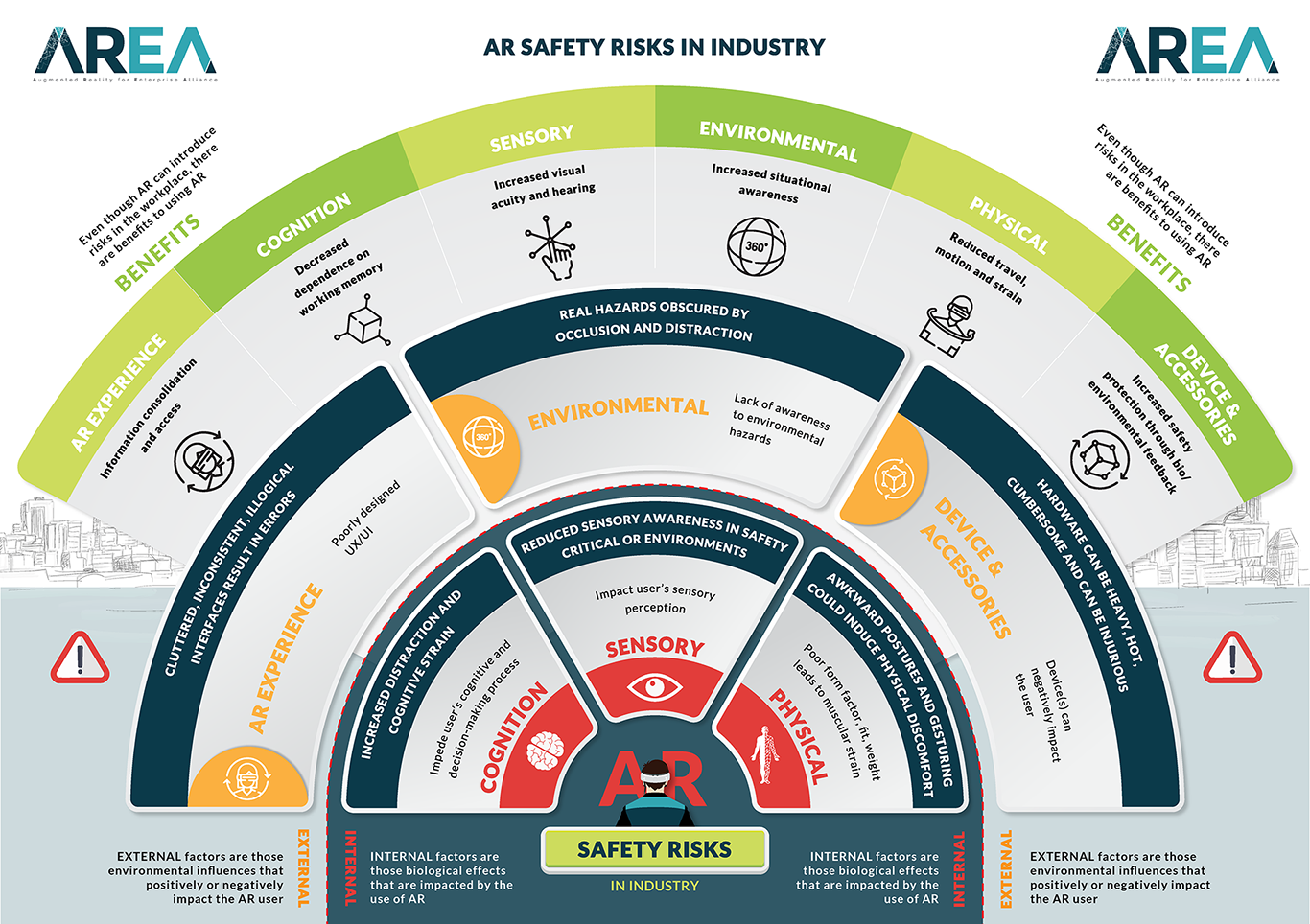
As AR introduces new ways of working, are there safety risks organizations should be considering? The member-led AREA Safety Committee has answered that question with the published AREA Safety Infographic.
The AREA Safety Infographic explores the potential safety risks of using AR, as well as the benefits of AR in the workplace. It is intended to be used as an educational tool for enterprises developing their AR plans. By giving careful consideration to safety before deploying AR solutions, organizations may be able to avoid issues before they occur.
The AREA would like to thank the Safety Committee and its co-chairs, Greg Garrett and Brian Laughlin (Boeing), supported by Amina Naqvi (MTC) and Richard Marklin Ph.D (Marquette University) for their expert input, insight and work to complete this infographic.
The AREA Safety Infographic was recently updated – we would like to thank the following organisations for their contributions – American Bureau of Shipping, Boeing, Dassault Systemes, Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, ExxonMobil, Lockheed Martin, Keen Research, Magic Leap Inc, MBDA, NIST.
How to use: The infographic has 12 sections for AR Safety. The sections contain the benefits and challenges related to the topic within AR. Each section has a summary to the left when it is clicked on. There is a detailed page for the section when clicking on the ‘LEARN MORE’ button.
Click on any section to view more information.
Augmented reality (AR) safety experiences offer several benefits. Firstly, they provide immersive training scenarios without real-world risks, allowing users to practice safety protocols in a controlled environment. Secondly, AR enhances retention through interactive simulations, improving knowledge retention and skill development. Thirdly, it enables real-time guidance, offering immediate feedback and assistance during critical tasks. Additionally, AR safety solutions can be customized to specific industries and hazards, addressing unique safety challenges effectively. Finally, these experiences promote proactive safety measures by fostering situational awareness and decision-making skills, ultimately reducing workplace accidents and injuries.
Augmented reality (AR) in the medical field boosts patients' cognitive abilities by employing AR tasks for cognition, mobility, and basic tasks. AR decreases cognitive load, aiding learning by freeing up working memory. It's seen to lower mental workload, enhance task performance, and reduce errors in medical and construction fields. AR augments vital information, easing comprehension compared to textbooks. While AR simplifies tasks through 3D models and spatial cognition, it poses new learning challenges. Research mainly focuses on AR's impact on task completion time and errors, leaving gaps in understanding its effectiveness across learning stages.
Reference: https://pubs.sciepub.com/education/9/8/6/index.html
Augmented reality offers diverse benefits spanning personal growth, education, and therapy. Immersive experiences enhance learning through interactive environments, aid skill development via simulations, and facilitate therapy for conditions like PTSD. Entertainment-wise, AR provides escapism through gaming and interactive theatre. It fosters empathy, innovation, and social interaction, encouraging creativity and teamwork. Moreover, AR creates memorable experiences, leaving lasting impacts on participants. Whether for learning, entertainment, or therapeutic purposes, augmented reality enriches lives by engaging users in immersive, interactive realms.
Augmented Reality (AR) offers multiple benefits, particularly in renewable energy and manufacturing sectors. In renewable energy, AR aids in understanding energy systems through MIT's 3D visualization platform, aiding informed decisions. It also facilitates training and simulation for engineers, minimizing risks and ensuring efficiency. Urban planning integrates AR to analyze phenomena like noise and pollution, enhancing decision-making for city managers. AR assists the packaging industry in sustainability efforts by reducing waste and engaging consumers with immersive experiences. In manufacturing, firms like Lockheed Martin utilize AR to streamline production, reducing errors, wastage, and resource strain, promoting sustainability.
Augmented Reality (AR) offers significant benefits in manufacturing. One key advantage is creating a safer and more comfortable work environment. AR enables hands-free task completion, reducing the need for workers to move around the workspace, thus minimizing physical strain. Additionally, AR enhances productivity by providing digital instructions and optimizing processes. Quality control is improved through AR's ability to detect and reduce non-conformities, saving time and resources. It also connects the virtual and real worlds, facilitating data interaction on the shop floor. Moreover, AR aids in skills development by offering intuitive training methods. Furthermore, it optimizes documentation, traceability, and reporting, ensuring better industrial efficiency.
AR headsets revolutionize interaction with digital content, offering hands-free operation for tasks requiring manual dexterity or multitasking. Equipped with sensors, they boost situational awareness, aiding navigation and hazard avoidance. Remote Assistance features enable collaboration with experts, crucial where on-site help is limited. Ideal for training, they simulate hazardous scenarios in industries like manufacturing and healthcare. Integrated with Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) like helmets, they merge physical protection with augmented information, ensuring safety in high-risk environments.
References: https://mixed-news.com/en/augmented-reality-hardware-and-definitions/#Mobile_AR
Augmented Reality (AR) faces several key challenges. Firstly, achieving context awareness is vital, tailoring information to user goals and location. This involves utilizing sensors like GPS and machine learning for interpretation. Secondly, maintaining visual clarity amidst real-world backgrounds is crucial, avoiding overwhelming the user's view. Thirdly, empowering user control is essential, allowing manipulation and interaction with AR content. Finally, ensuring user comfort and safety is paramount, minimizing discomfort such as eye strain and nausea. This involves adhering to ergonomic principles and providing adjustable settings.
Augmented reality (AR) technology presents environmental concerns such as high energy consumption for device operation and content creation, leading to increased carbon emissions. Manufacturing and disposal of AR devices contribute to electronic waste and resource depletion. Moreover, excessive AR use may exacerbate digital addiction and overconsumption. Addressing these issues requires energy-efficient device design, sustainable content creation practices, and responsible consumption habits.
Addressing safety challenges in augmented reality (AR) necessitates a multifaceted approach. It involves leveraging technological advancements, educating users, regulating the technology, and fostering industry collaboration. Key concerns include distraction, physical hazards like compromised vision, motion sickness, fatigue from device weight, cybersecurity risks due to connectivity, and legal/ethical dilemmas regarding privacy and consent. AR's immersive nature poses risks such as distraction during tasks like driving, obstructed peripheral vision, motion sickness, and cybersecurity threats. Additionally, legal and ethical considerations arise concerning privacy infringements in public spaces. Mitigating these risks is essential for responsible AR development and deployment.
References: https://mixed-news.com/en/augmented-reality-hardware-and-definitions/#Mobile_AR
Cognition issues in augmented reality (AR) encompass challenges related to perception, attention, memory, and decision-making. These issues stem from the integration of digital information into the user's perception of the physical environment. AR can strain cognitive resources, leading to distractions, reduced attentional focus, and information overload. Memory retrieval may be hindered by the blending of virtual and real-world elements, affecting task performance and learning. Moreover, the interpretation and integration of AR content require cognitive effort, potentially leading to errors or misunderstandings. Understanding and addressing these cognition issues are crucial for optimizing user experience and ensuring safe and effective AR utilization.
Reference: https://pubs.sciepub.com/education/9/8/6/index.html
Sensory issues in augmented reality (AR) encompass challenges related to the integration of virtual sensory stimuli with real-world sensory input. These issues arise due to discrepancies between the information presented by AR devices and the user's sensory experiences. Visual sensory issues include occlusion of real-world objects, perceptual mismatches, and visual fatigue. Auditory sensory issues involve sound localization and the blending of virtual and real-world auditory cues. Additionally, tactile feedback in AR may be limited or absent, impacting user interaction and immersion. Addressing these sensory issues is essential for enhancing user experience, reducing discomfort, and maximizing the effectiveness of AR technology.
Physical challenges in augmented reality (AR) encompass obstacles related to the interaction between users and AR hardware, as well as the impact of prolonged usage on the body. These challenges include ergonomic issues such as discomfort or fatigue from wearing AR devices for extended periods, especially if they are heavy or poorly fitted. Additionally, users may face obstacles navigating physical spaces while wearing AR headsets, risking collisions or accidents due to compromised peripheral vision or spatial awareness. Ancillary equipment like battery packs or cables can also pose physical hazards. Addressing these challenges involves designing lightweight, ergonomic AR hardware and promoting user-friendly interfaces to enhance safety and usability.