Best Practices Guidance for AR Professionals
As Augmented Reality introduces new ways of working, are there security risks organizations should be considering? The member-led AREA Security Committee has answered that question with the AREA Security Infographic.
The AREA Security Infographic explores the potential security risks of using AR, as well as the benefits of AR in the workplace. It is intended to be used as an educational tool for enterprises developing their AR plans. By giving careful consideration to security before deploying AR solutions, organizations may be able to avoid issues before they occur.
The AREA would like to thank the Security Committee and Tony Hodgson, CEO of Brainwaive LLC for their expert input, insight and work to complete this infographic.
The AREA Safety Infographic was recently updated – we would like to thank the AREA Security Committee and its chair James Cooper (RTX) for their contributions.
How to use: The infographic has 10 sections for AR Security. The sections contain the risks and considerations related to the topic within AR. Each section has a summary to the left when it is clicked on. There is a detailed page for the section when clicking on the ‘LEARN MORE’ button.
Click on any section to view more information.
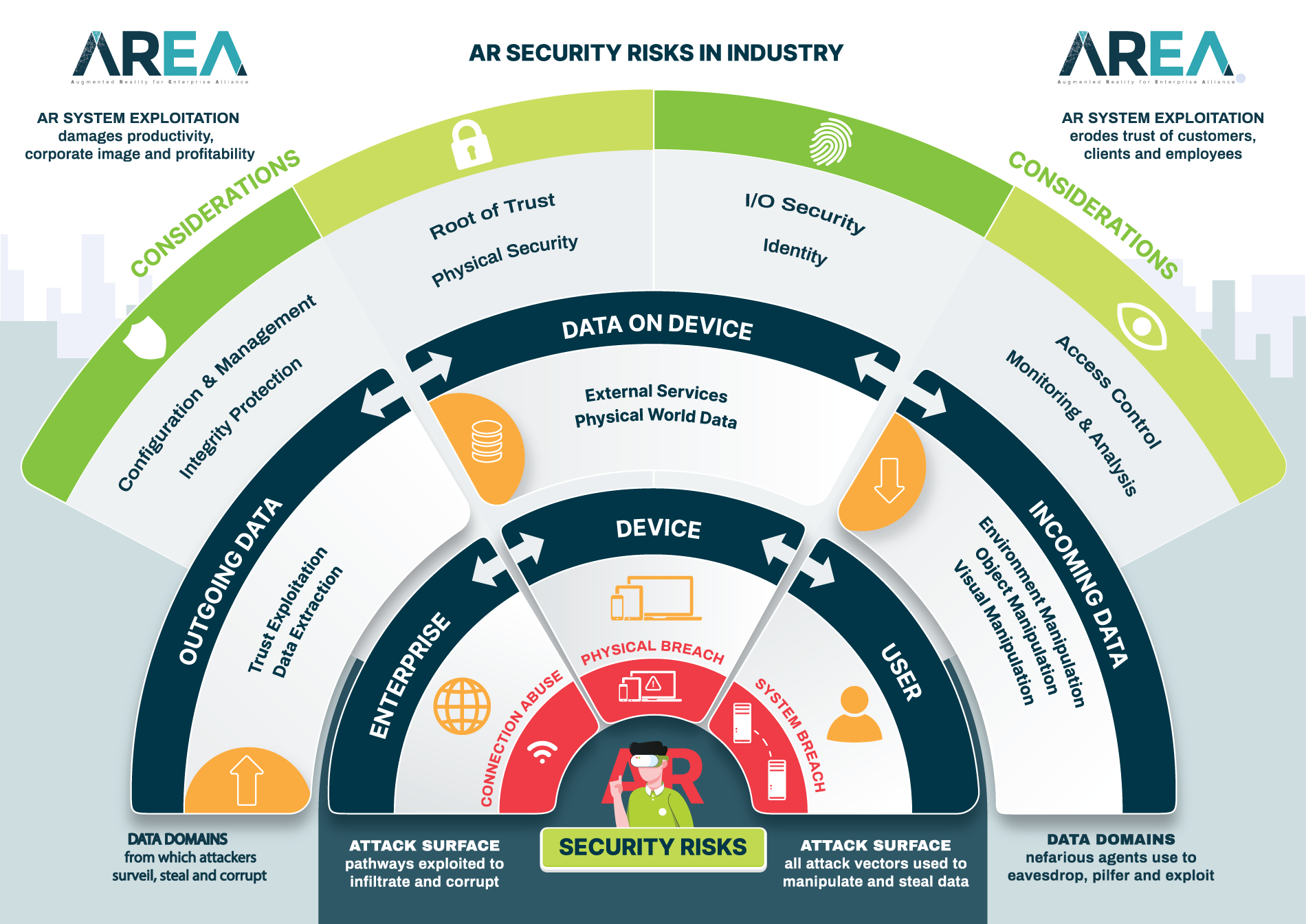
AR devices, due to their unique hardware and complexity, require a hardware root-of-trust for core security functions. This ensures the device's integrity, protects data storage, and isolates processes for maximum security.
AR devices need anti-tamper tech and secure ports for physical security. Perimeter defenses are helpful, but consider their mobility and size.
AR's unique hardware and data collection require careful security assessment of all components (hardware, software, sensors) to minimize confidentiality, integrity, and availability risks.
For secure management and access control, AR devices need unique identities (one per device) plus options for multiple support and owner identities, all with varying security levels.
AR's new voice, gesture and gaze controls make strong passwords difficult for secure access. Biometrics offer a solution but integrating them securely company-wide is complex.
AR devices should create a secure log of important system events (think "audit trail") that can be protected with encryption or stored securely depending on the specific needs.
AR devices pose unique security challenges due to their ability to interact with the physical world. Penetration testing these devices requires replicating their real-world use to uncover vulnerabilities. Attackers could exploit AR features like spatial mapping to bypass security measures or capture sensitive data through video and image capture. This framework helps identify these risks and guide penetration testers in securing AR devices.
AR devices collect a vast amount of user data through cameras, sensors, and microphones. This data can include gestures, eye movements, voice, location, and even thermal signatures. Companies using AR devices need a clear data policy outlining what's collected, how it's used, and security measures. AR devices should also allow remote data wiping and encrypt data for confidentiality.
AR devices introduce unique security risks for businesses. Unlike traditional IT systems, AR devices collect real-world data (audio, video, location) that attackers can exploit. This data allows attackers to bypass security measures or gain access to non-connected systems (e.g., eavesdropping passwords on air-gapped systems). To address these risks, companies should consider AR's specific data collection capabilities and how they might be exploited.
AR devices connect like many mobile devices (WiFi, Bluetooth, NFC). While specific security profiles depend on your setup, it's important to understand the network connections and potential threats at all levels. Periphals may also have weak authentication, creating more vulnerabilities. To communicate these risks clearly, a common language for attack categories is recommended. The document outlines two main categories: Functionality Misuse (abusing device features) and Access Control Subversion (compromising logins or security).
AR devices pose unique security risks because they collect real-world data (audio, video, location) unlike traditional IT systems. This data can be stolen by attackers (eavesdropping passwords, stealing tokens) to bypass security or attack separate systems. AR data collection (footprinting, interception) is a major concern. To address these risks, a common language for attack categories is recommended. This document outlines two main categories: Data Capture (stealing AR device data) and (already mentioned) Functionality Misuse/Access Control Subversion (abusing device features or compromising logins).
AR devices introduce new security risks beyond those of mobile devices. These risks come from how AR devices interact with the real world (collecting data like audio and video) and their complex software (combining mobile OS, middleware, and custom apps). Existing mobile security practices aren't enough. To secure AR devices, stakeholders need to understand these new threats and develop strong security protocols for all software components and communication channels.
AR devices face mobile device security challenges, including logging, malware detection, and incident response. Ensuring security requires host-based protection, image management, and consistent device images. Lifecycle policies should include identity management.
AR systems need protection like standard devices (malware detection) but also special protections due to their unique features. To achieve this, the system should run applications at standard user levels and keep device protection at higher, root levels.
AR headsets pose unique security risks for businesses. Traditional mobile security isn't enough. Vendors, IT departments, and users all share responsibility for securing AR. AR devices constantly collect data (audio, video, location) that can be exploited. They also require complex authentication methods due to voice and gesture controls. To address these risks, all stakeholders need to work together to create a comprehensive security plan for AR deployments. This section is a first step, and further collaboration is needed to develop strong security protocols.